Cesarean Section
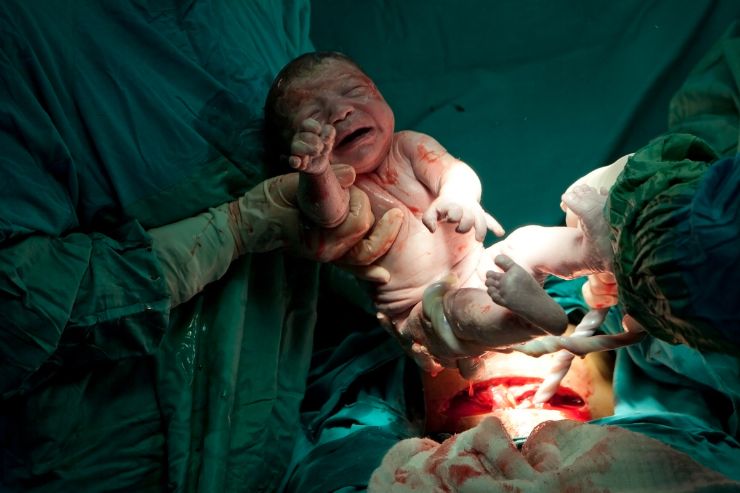
A Cesarean section (C-section) is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through an incision in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. This method is typically recommended when a vaginal delivery would pose a risk to the mother or baby. Common reasons for a C-section include prolonged labor, fetal distress, placenta previa, breech presentation, or multiple pregnancies. While a C-section is generally safe, it is considered major surgery and requires a longer recovery period compared to a normal vaginal delivery.
During a C-section, the mother is usually given regional anesthesia, such as an epidural or spinal block, which numbs the lower part of the body while allowing her to remain awake and aware during the procedure.
The surgery typically takes about 45 minutes to an hour. After the baby is delivered, the surgical team carefully closes the incisions. Postoperative care involves monitoring for signs of infection, managing pain, and supporting the mother’s recovery as she adjusts to caring for her newborn. Despite the longer recovery time, a C-section can be a life-saving procedure that ensures the safety and well-being of both mother and baby when complications arise.
